Underactivity of the thyroid gland, namely hypothyroidism, is a disease caused by the inability to produce thyroid hormones in sufficient amounts.
İçindekiler
What Is Hypothyroidism?
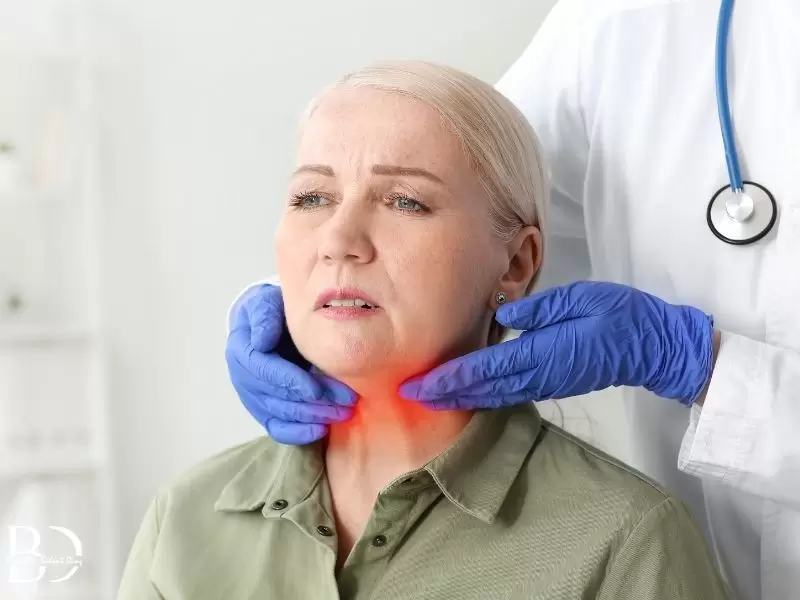
In the case that the thyroid gland cannot produce the thyroid hormones required for the body in sufficient amounts as a result of underactivity of the thyroid gland, this is called “hypothyroidism.” Due to an underactive thyroid gland, conditions such as fatigue, weakness, dryness and rashes on the skin, enlargement of the tongue, voice changes, and similar issues may be seen.
Hypothyroidism, which can be detected with blood tests, is a disease that must be treated. People who have been experiencing one or more of the symptoms for a certain period of time should consult a doctor and have their blood values examined.
What Causes Hypothyroidism?
As in our country, the most common cause of hypothyroidism in the world is insufficient iodine intake. Iodine forms the building block of thyroid hormones. In addition, autoimmune diseases (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis), hyperthyroidism treatment, radiation therapy, pituitary gland disorders, and previous thyroid surgery constitute other causes of hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism may be caused by factors that prevent or reduce the proper functioning of the thyroid glands. Hashimoto’s disease, one of the autoimmune diseases and a common one, may cause this disease because it damages the thyroid gland. Having received radiation therapy, long-term use of certain medications, iodine deficiency, deficiencies seen in a person after childbirth, congenital functional disorders, and similar conditions may also cause hypothyroidism.

What Are the Symptoms of Hypothyroidism?
Since thyroid hormones regulate metabolism in the body, in cases of deficiency many systemic findings and complaints may occur. These complaints are;
- Abnormal weight gain
- Fatigue
- Constipation
- Menstrual irregularity
- Hair loss,
- Cold intolerance
- Slowing of the heart rate
- Difficulty concentrating, weak memory
- Dry skin
Diagnosis of Hypothyroidism
Diagnosis of hypothyroidism primarily begins with the patient’s history and physical examination. Then, thyroid function tests are requested from patients who raise suspicion in diagnosis. T3, T4, and TSH tests are the first examinations evaluated. According to their results, a diagnosis of hypothyroidism may be made. In addition, thyroid ultrasound, thyroid scintigraphy, and, if necessary, thyroid fine-needle biopsy may also be used for investigations aimed at the cause. The examination performed to measure thyroid functions is a blood test, and hormone levels are evaluated in this blood test. A blood test is sufficient for diagnosis. A diagnosis can be made by examining the level of TSH hormone in the blood and the level of T4 hormone. If TSH is higher than it should be and the thyroid hormone called T4 is low in the blood, it can be said that the person has hypothyroidism.

How Is Hypothyroidism Treatment Applied?
In the treatment of hypothyroidism, synthetically produced thyroid hormone preparations are used. After treatment starts, the drug dose is tried to be adjusted by looking at the blood levels of thyroid hormones after a while. This period may take weeks in some patients. When hypothyroidism is not treated, systemic metabolic problems begin to occur. Among these, life-threatening complications such as enlargement of the heart walls, heart failure, hypertension, arteriosclerosis, and blood clot formation in vessels may be seen. If you have one or more of the specified findings, you should seek help from a specialist physician on the subject.
Is Hypothyroidism Dangerous?
Treating hypothyroidism is of great importance because if it is not treated, the patient’s condition may become dangerous. This disease, which affects metabolism, may cause goiter disease. If goiter disease progresses, breathing and swallowing problems may be seen in the person. Another problem that may be seen is heart problems. Hypothyroidism increases the level of LDL, which is also called bad cholesterol. In this case, it may cause serious diseases related to the heart. An increase in LDL cholesterol may cause diseases such as heart enlargement and heart failure, which can create a life-threatening situation. In addition to these disorders, psychological and mental health problems, infertility, peripheral neuropathy, and similar conditions may also be seen in the person.
Related content: Scarless Closed Thyroid Surgery